Difference Between FRT and FR Cable
LSZH Flame Retardant (FRT) and LSZH Fire Resistant (FR) cables are often confused, but they serve different fire safety purposes.
Although the words flame and fire are commonly used interchangeably, the real difference lies between retardant and resistant. Understanding this distinction helps ensure the right cable is selected for each application.
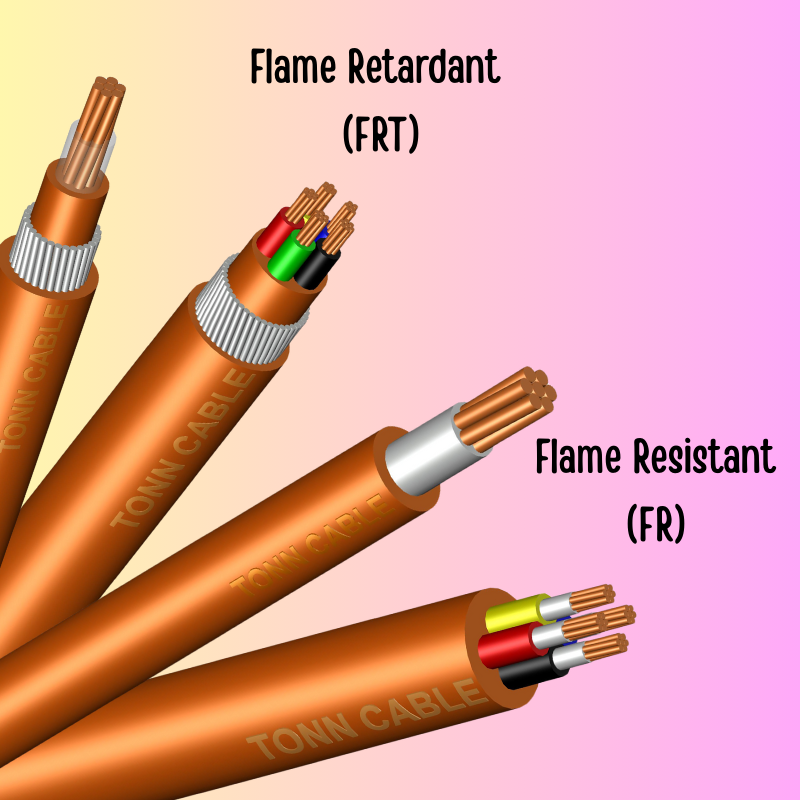
LSZH Flame Retardant (FRT) Cable
LSZH FRT cable is designed to slow down the spread of fire, but it does not continue to function electrically during a fire.
These cables are tested according to international flame propagation standards such as:
-
IEC 60332-1-2 (single cable test)
-
IEC 60332-3 (bunched cable test)
To improve safety, FRT cables use LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) materials, which produce minimal smoke and no corrosive gases when burned. As a result, they also comply with:
-
IEC 60754 / BS EN 60754 (acid gas emission tests)
-
IEC 61034 / BS EN 61034 (smoke density tests)
LSZH FRT cables are commonly used in enclosed or high-occupancy areas such as airports, hospitals, schools, hotels, underground transport systems, and high-rise buildings.
LSZH Fire Resistant (FR) Cable
LSZH FR cable provides a higher level of protection. It not only limits the spread of fire but also maintains circuit integrity during a fire.
These cables include a mica tape layer around the copper conductors. Mica is a non-combustible mineral with excellent heat resistance and electrical insulation properties. During a fire, it acts as a protective barrier, allowing the cable to continue operating.
In addition to standard LSZH FRT tests, FR cables are tested to:
-
SS 299 / SS 299-1
-
BS 6387
-
IEC 60331
These tests assess the cable’s ability to withstand fire, fire with water, and fire with mechanical impact.
LSZH FR cables are essential for critical systems that must remain operational during emergencies, such as fire alarm systems, emergency lighting, and voice evacuation systems.
What is Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH)?
To understand LSZH, it is helpful to compare it with PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), a commonly used cable material.
When PVC burns, it releases thick black smoke and hydrogen chloride gas (HCl). The smoke reduces visibility, while HCl gas can form hydrochloric acid upon contact with moisture, causing severe irritation and hindering evacuation.
LSZH materials contain inorganic additives such as aluminium hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide. When exposed to fire, these materials release water vapour, helping to suppress flames and reduce oxygen availability.
As a result, LSZH cables produce low smoke, minimal toxicity, and non-corrosive gases, improving visibility and safety during fire evacuation.