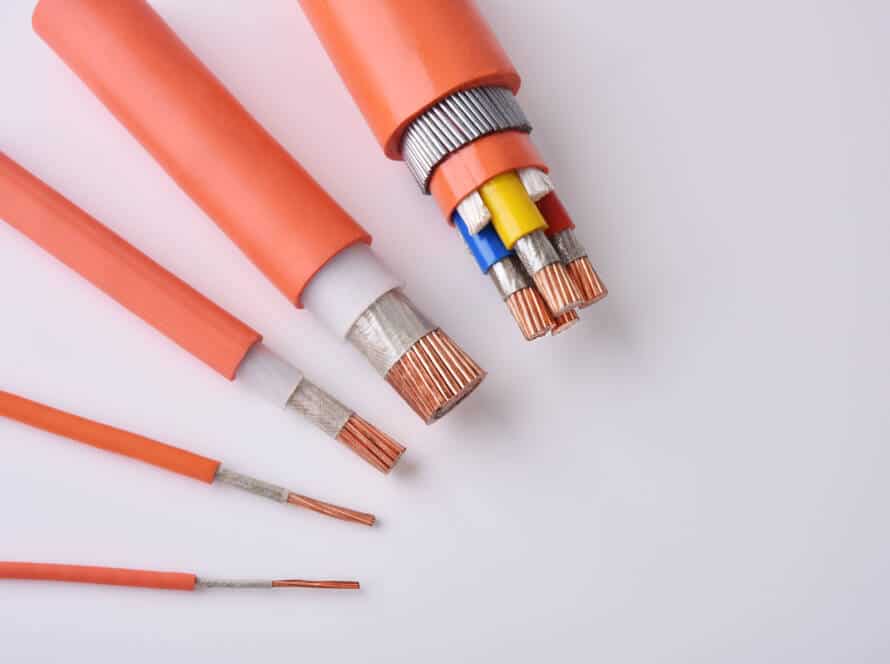
In summary, if you have acquired a cable that meets international standards and has been installed indoors following the appropriate guidelines, you can typically anticipate that your cables will have a lifespan designed to last at least 20 to 30 years.
What factors can influence the lifespan of a cable?
Numerous operational and environmental factors can significantly influence the lifespan of a cable. These factors include:
1.Instances of overload or short circuits can lead to a reduction in the cable’s longevity.
2.The proximity of the cable to high heat sources, such as being installed in elevated ambient temperatures not previously considered, or being situated adjacent to other circuits that were not accounted for during the cable sizing process.
3.Exposure to outdoor elements, including UV radiation or adverse weather conditions, which may not have been included in the original design, can also impact the cable. Additionally, if water penetrates the cable core or if there is an unexpected pest infestation, these factors can further compromise its integrity.
4.The presence of contaminants, oils, or acids can deteriorate the sheath or insulation of the cable.
5.Mechanical stresses, such as tensile forces, vibrations, or bending that occur during or after installation, can also affect the cable’s performance.
International organizations like the IEC and BS EN, along with national standards such as Singapore Standards (SS), have established cable standards that assess performance across various applications. While these standards do not explicitly define the lifespan of manufactured cables, they include both electrical and non-electrical tests that suggest a lifespan of at least 20 to 30 years under typical indoor conditions. This provides end users with confidence regarding the service life of cables that come with a Certificate of Compliance to the relevant national or international standards.
To maximize the lifespan of electrical cables, it is crucial to mitigate the impact of the aforementioned operational and environmental factors. Selecting the appropriate insulation and sheath materials based on the specific cable application, as well as ensuring correct cable sizing, are essential steps in this process.