What role does cable insulation play?
Cable insulation serves as a crucial protective layer for the conductors within cables. It is designed to be non-conductive, effectively preventing electrical leakage, ensuring that conductors do not come into contact with one another, and safeguarding the conductor from environmental hazards such as heat, moisture, and chemicals. Inadequate or compromised insulation can lead to serious issues, including short circuits, electric shocks, or even fires.
What is an Insulation Resistance (IR) Test?
An insulation resistance (IR) test evaluates the resistance to electrical current flow within a completed cable. By applying a test voltage, this assessment determines the effectiveness of the insulation in preventing electric current from escaping. This process can be likened to using pressurized water in a pipe to detect any leaks.
As insulation materials age over time, the differences in performance between high-quality and lower-quality insulation become increasingly noticeable. Therefore, it is crucial to achieve a satisfactory pass rate on the IR test following cable manufacturing to ensure the cable’s durability and longevity.
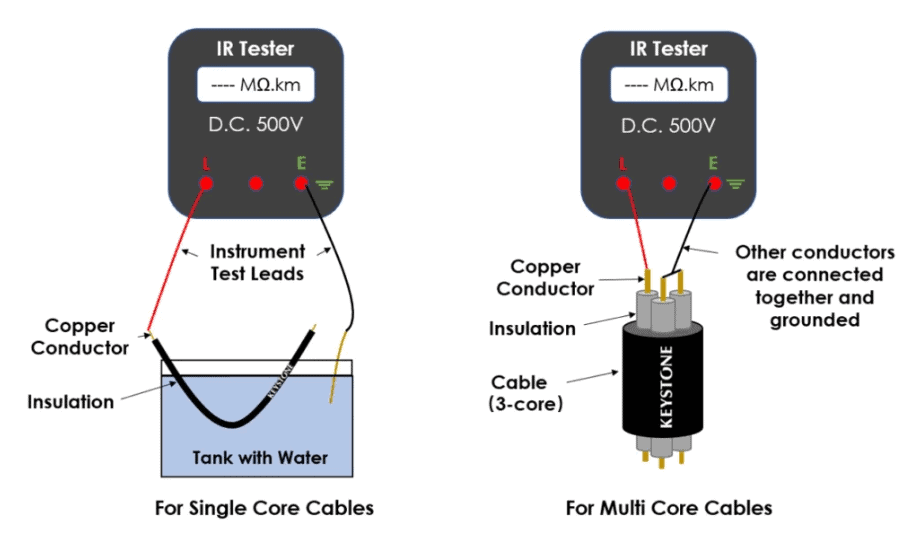
Insulation Resistance Testing Procedure
The Insulation Resistance (IR) test is performed utilizing an IR tester, which is a portable ohmmeter (MΩ.km) equipped with an integrated generator that produces a high direct current (DC) voltage. Typically, this voltage is set at 500V, facilitating the flow of current along the insulation’s surface. The resistance measurement obtained reflects the leakage current; a high IR value indicates minimal current leakage through the insulation, whereas a low IR value suggests significant leakage, potentially signalling a fault in the insulation.
At Tonn Cable’s quality control laboratory, we strictly follow the International Standards IEC 60502-1 for conducting our IR tests. For a cable to pass, it must achieve a minimum insulation resistance constant Ki (as detailed in the table below) when tested at its maximum operating temperature, which is 70 °C for PVC insulated cables and 90 °C for XLPE and rubber insulated cables.

For single core cables, testing is conducted in water, whereas multi core cables undergo testing in air. Additionally, test outcomes can differ based on various factors such as insulation type, cable length, and surrounding temperature.




